Five generations of computer: : First generation (1940-1956), Second generation (1956-1963), Third Generation (1964-1971), Fourth Generation (1971-2010), Fifth Generation, Conclusion.
Technology does not need any explanation as we all are well aware of it and it is growing and growing. When you think about the time of evolution of technology then we get startled as it happened in such a minuscule time.
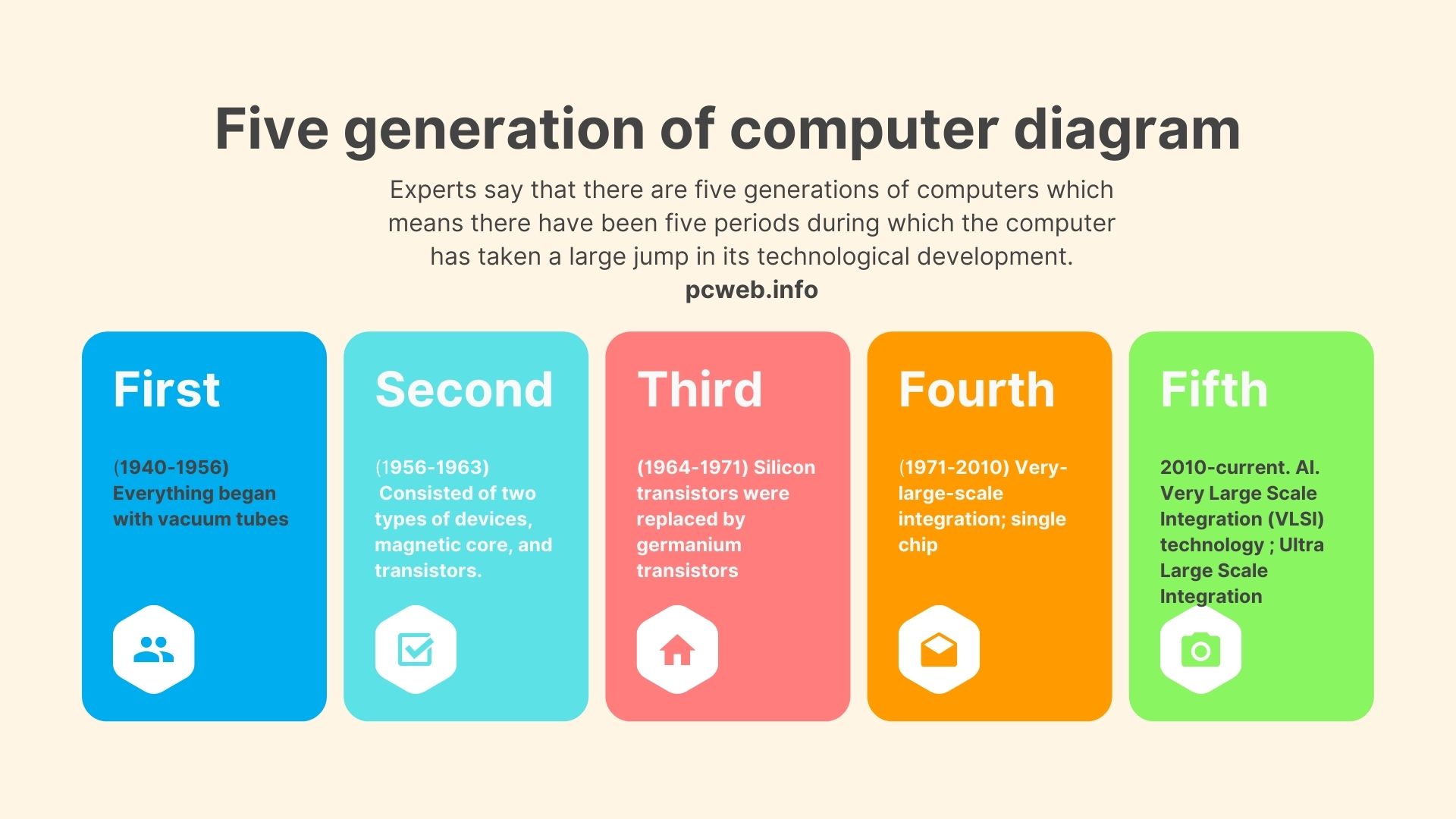
Experts say that there are five generations of computers which means there have been five periods during which the computer has taken a large jump in its technological development.
Let’s have a look at the description of all five generations to know how time evolves and how we have passed through all the generations to the current one.
First Generation (1940-1956)
Everything began with vacuum tubes. Similarly, the first generation of computers also started with vacuum tubes. These vacuum tubes generate a lot of heat and due to the consumption of a great deal of electricity, these tubes were expensive to operate.
The machines with vacuum tubes are prone to malfunctioning frequently and due to frequent malfunctioning, they always required constant maintenance. The first generation of computers was difficult to program as it used to be operated on machine language.
In the first generation of computers, vacuum tubes were used for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory. The input was given to the computer through paper tubes and punched cards and the output was used to be displayed as printouts.
The instructions were given in machine language using 0s and 1s for the coding of instructions. It can be considered as a drawback of the first generation of computers as it can only solve the problem at a time and the computation time was in milliseconds.
These computers were extraordinarily large and needed a large room for installations. They were in common use for scientific applications as they were the fastest computing devices of that time. For instance, Electronic Numerical Integrator And Calculator (ENIAC).
Second Generation (1956-1963)
The second generation of computers consisted of two types of devices, magnetic core, and transistors. It was because of these transistors that better computers were developed than the first generation of a computer consisting of vacuum tubes.
These transistors replaced the vacuum tubes reducing their size. These computers become faster, cheaper, reliable, and energy-efficient. For primary memory, magnetic core technology was used in second-generation computers and magnetic disks and magnetic tapes were used for secondary storage.
These computers too generated a lot of heat but less than the first generated computers and their maintenance rate was also low as compared to first-generation computers.
The input was given through punched cards and output using printouts. In second-generation computers, the concept of the stored program was in use where instructions were stored in the memory of the computer.
In comparison with a first-generation computer, the instruction of second-generation computers was written using assembly language. Assembly language makes use of mnemonics SUB for subtraction, ADD for addition for the coding of instruction.
Instruction is easy to write in assembly language as compared to machine language. The computation of second-generation computers was in microseconds.
The size of the computer was reduced although the cost of commercial production was still high but less than that of first-generation computers they required frequent maintenance too alongside frequent cooling.
The transistors in second-generation computers were to be assembled manually. For instance, PDP-8, CDC 1604, and IBM 1401.
During the era of second-generation computers, High-level languages such as the early version of COBOL and FORTRAN were also developed.
Third Generation (1964-1971)
The period for the third generation of computers started in 1964 and lasted till 1971. During the development of third-generation computers, silicon transistors were replaced by germanium transistors.
Integrated circuits were developed with the use of interconnecting transistors and capacitors and resistors were made on a single chip of silicon. These integrated circuits were small in size and they were used in computers because of low consumption of power and their commercial cost was less than the previous switching technology.
The advancement in storage technology directed in creating large capacity magnetic tapes and disks. This advancement also resulted in large magnetic core-based random access memory. High-level languages were further improved. Languages such as Fortran IV and Fortran compilers were also developed. Another major development of this period was the standardization of COBOL (COBOL 68).
Some advantages of the third-generation computer that you should be reminded of are that it contains all the proper functions if operating for general purpose. Third-generation computers can be used for high-level machinery. They have more battery accuracy than the previous generations. In these keyboards and mice were used for the input of information and data.
Some instances of third-generation computers are IBM 360/370. CDC 6600, TDC-316, IBM-370/168, Honeywell-6000 series, and PDP (Personal Data Processor).
Fourth Generation (1971-2010)
The topic of the generations of computers is of prime importance. With time we have seen development in physics and electronics. As of now, we have discussed the three generations of computers. How about knowing about the fourth generation too.
The fourth generation of computers began after the end of the third generation of computers in 1971 and continued till 2010. During the introduction of the fourth-generation very-large-scale integration, technology was found.
Surprisingly tens of thousands of components were made of the size of a fingernail that can be easily packed on a single chip. With the invention of these small chips, the development of microprocessors also took place. Semiconductor memories replaced the magnetic core memories. The Personal Computers (PCs) operating system was developed during the fourth generation of computers.
Graphical User Interface was exploited to offer more advanced comforts to the users. The PCs were tagged with reasonable prices. Significant development of this period was the development of concurrent programming languages such as ADA. Interactive graphic devices and language interfaces to the graphic system were also introduced.
The advantages of the fourth generation of computers over the previous generation that made it one of the best-selling devices were that it was constructed with fast processing power and low power consumption. It needs less repair as compared to the previous one.
Fourth Generation Computers are used for commercial production and all types of High-level languages including DBASE, C++ can be used in this computer. It consists of a fan for releasing heat and keeping the system cold. VLSI technology was in use during the fourth generation.
The examples of the fourth generation of computers are STAR 1000, DEC 10, PDF 11, CRAY-X-MP (SuperComputer), and CRAY-1 (Supercomputer).
Fifth Generation (Current)
The fifth generation of computers defines a new super-breed of computers. These computers can think and can make decisions themselves and new improvements are assumed to be introduced in the future.
Artificial intelligence is being built into these computers. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) technology is making way for Ultra Large Scale Integration. This technology will be helpful in the development of a microprocessor chip containing several million electronic components on each.
During this period desktops and powerful laptops, notebooks PCs were introduced. Instead of conventional Von Neumann architecture, revolutionary parallel processing is used in these supercomputers.
Efforts are going on for developing new programming languages to cope with these new generation computers. Moreover, functional language and object-oriented languages such as C++ are the development of this generation. Moreover, user-friendly operating systems like Linux, MS Windows, and Linux-based software are also the introduction of this period.
The advantages of the current generation computer over the previous generation are:
These computers are portable and easy to use and show development in parallel processing as well as superconductor technology. They have opened new doors for artificial intelligence.
They are much smaller in size and can be carried anywhere and their fast speed of processing differentiates them from other computers. These computers are much faster than previous ones and efforts are going on for further advancement.
Although fifth generation computers are most useful and on the basis, it will be unfair to categorize them with others but these computers have some disadvantages too. They supply much power to companies for see what everyone is doing and this great supply of power may infect their computers. Likely, these computers are tending to be sophisticated and complex tools.
The examples of the fifth generation of computers are word processors that could be controlled by speech, an intelligent system controlling the route of missile and defense-system that can look after attacks, and the programs translating documents from one language to another.
Conclusion: Five Generations of Computer
It is hoped that with the progress of this generation computers can be fed with such systems that they can learn self-organization which sound quite interesting in case if the organization isn’t coming naturally to you. The biggest advancement up-to-date is the introduction of artificial intelligence which has fitted into modern technology as it was always needed.
Getting to know about all five generations clarifies the thoughts that it is not the end of advancement and technology and with time, new things will continue to pop up.
This interesting article is a great deal of reading as we hope you will like it.
Read also: Digital marketing history, evolution, timeline, chronology ; Ontology in Information Science; 6TH GENERATION OF COMPUTERS; Differences between Chromebook and Laptop
External resources: webopedia